Running LP API binary
Before you do anything, you need to generate a valid signing_key and fund the associated account.
Using the pre-compiled binaries
Download the lp-api software and the chainflip-node:
apt-get install chainflip-lp-api
apt-get install chainflip-nodeCommand line arguments
- The
state_chain.ws_endpointshould point at a synced Chainflip State Chain RPC node. The default isws://localhost:9944— assuming it is run locally. - The
state_chain.signing_key_fileshould be a path to a file containing the hex-encoded private key for the on-chain LP account. The default file path is/etc/chainflip/keys/signing_key_file. The account should be funded and the account role should be set to LP. - The
portis the port on which the LP API will listen for connections. Use0to assign a random port. The default is80. - New functionality available from version 1.7+: The
health_check.hostnameandhealth_check.portdescribe the hostname and port where the LP API will listen for health check requests. Both arguments have to be specified for the health check server to start.
./chainflip-lp-api --helpchainflip-lp-api
USAGE:
chainflip-lp-api [OPTIONS]
OPTIONS:
-h, --help
Print help information
--health_check.hostname <HEALTH_CHECK_HOSTNAME>
Hostname for this server's health check. Requires the <HEALTH_CHECK_PORT> parameter to be
given as well.
--health_check.port <HEALTH_CHECK_PORT>
Port for this server's health check. Requires the <HEALTH_CHECK_HOSTNAME> parameter to be
given as well.
--port <PORT>
The port number on which the LP server will listen for connections. Use 0 to assign a
random port. [default: 80]
--state_chain.signing_key_file <SIGNING_KEY_FILE>
A path to a file that contains the LP's secret key for signing extrinsics.
[default: /etc/chainflip/keys/signing_key_file]
--state_chain.ws_endpoint <WS_ENDPOINT>
The state chain node's RPC endpoint. [default: ws://localhost:9944]
-v, --version
Print version informationFor a full list of command line arguments, see chainflip-lp-api --help and chainflip-node --help.
To use the default configuration, run:
chainflip-node --chain /etc/chainflip/perseverance.chainspec.json --rpc-methods=unsafe
chainflip-lp-api --state_chain.signing_key_file /path/to/my/signing_key_fileUsing Docker
For a quick start with LP API, we have provided a docker-compose setup that runs the LP API and a State Chain node.
Registering the account
After being funded, before you can fully interact with the LP API, your account needs to be registered as a Liquidity Provider account.
Deployment Schema
LPs (and Brokers) should ideally run their own local RPC nodes. These nodes connect to the network and expose the LP & Broker APIs locally to the backend they want to use.
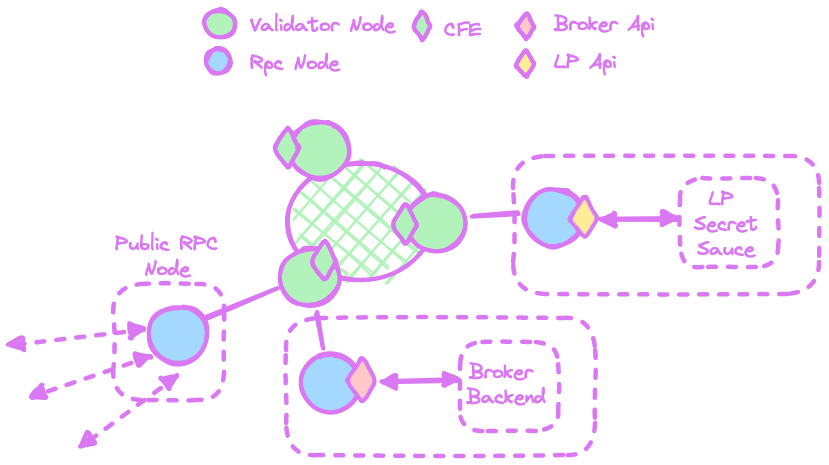
Avoid using the public RPC node since its particularly vulnerable to DDOS or other various attacks
Working Example
- Run the LP API server with the following command:
./chainflip-lp-api \
--state_chain.ws_endpoint ws://localhost:9944 \
--state_chain.signing_key_file /path/to/my/signing_key \
--port 80 # or whatever port you want to useIt will print 🎙 Server is listening on 0.0.0.0:80. and continue to run.
- In another terminal: Register as an liquidity provider if you are not already.
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "lp_register_account", "params": [0]}' \
http://localhost:80Returns {"jsonrpc":"2.0","result":null,"id":1}
- Request a liquidity deposit address:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "lp_liquidity_deposit", "params": ["Eth"]}' \
http://localhost:80The response is a hex-encoded deposit address: {"jsonrpc":"2.0","result":"0x350ec3dfd773978277868212d9f1319cbc93a8bf","id":1}.
Limitations
- The current API architecture supports only
wsand notwss.
Troubleshooting
LP API crashing
If your LP API crashes upon startup or when submitting requests, please ensure that you have updated it to the latest version. Make sure the version aligns with the specified engine and node versions. You can verify this easily using the —version command.